Mini-ITX boards: Advantages and Disadvantages of Industrial Use
What Mini-ITX features are required for industrial applications?
Industry requirements for Mini-ITX boards
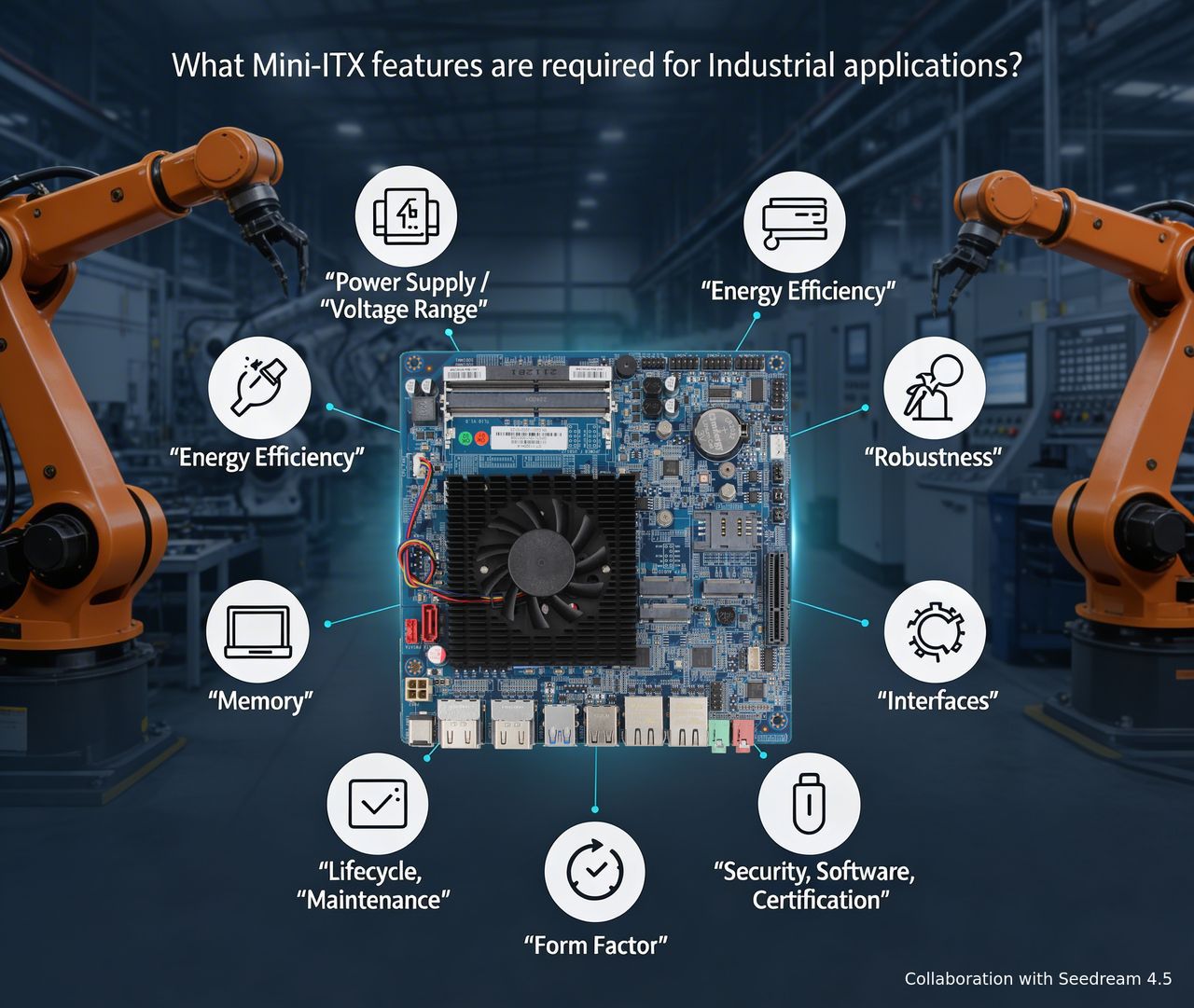
Industrial features of Mini-ITX boards
The following requirements are essential:Power Supply, Energy Efficiency, Robustness, Interfaces, Memory, Lifecycle, Maintenance, Security, Form Factor
Last updated: 19.02.2026
For industrial applications of Mini-ITX boards, certain industrial features are crucial. From an industry perspective, the following requirements are essential:
Power Supply / Voltage Range
• Wide input voltage ranges (e.g., 9–36 V, 12–24 V, 18–36 V) for direct connection to vehicle electrical systems, battery systems, or industrial 24 V power supplies.
• Integrated DC-DC converters with protection functions (overvoltage, undervoltage, reverse polarity, short circuit).
• Support for power profiles of different CPUs (T/TE/embedded variants), often with a configurable TDP limit in the BIOS.
• Support for always-on/ignition functions (e.g., in vehicles), time-delayed power on/off.
Energy Efficiency
• Selection of CPUs with different TDP classes (e.g., 6–15 W, 25 W, 35 W) to suit the application.
• Optimized voltage regulator modules (VRMs) for continuous 24/7 operation and low power consumption.
• Option for fanless operation with a large heatsink or case cooling design (heat spreader, heat pipe).
• Power management features: deep sleep states, Wake-on-LAN, Wake-on-Timer, and RTC wake for low-energy standby modes.
Robustness
• Extended temperature ranges (e.g., -20 to +70 °C or -40 to +85 °C).
• Protection against vibration and shock (reinforced solder joints, screw-locked connectors, soldered RAM/Flash where required).
• Partial conformal coating (protective lacquer) against moisture, dust, and salty air.
• Long 24/7 continuous operation with specified MTBF, suitable for continuous loads in industrial environments.
Interfaces
• Multiple Gigabit Ethernet ports (some PoE-enabled, some with TSN support for real-time networks).
• Numerous serial interfaces (RS-232/422/485) for PLCs, sensors, actuators, and legacy devices.
• Digital inputs/outputs (GPIO), relay outputs for direct control.
• Fieldbus/industrial protocols via on-board interfaces or modules (e.g., CAN, PROFIBUS, Modbus, EtherCAT via expansion).
• Multiple display outputs (LVDS/eDP/DisplayPort/HDMI) for panel PCs, HMI terminals, and digital signage.
• Internal expansion options (miniPCIe, M.2, mSATA) for WiFi/4G/5G, additional I/O cards, and SSDs.
Memory
• Support for both SO-DIMM RAM and soldered memory under shock/vibration conditions.
• Industrial-grade SSD interfaces (SATA, M.2) with support for pSLC/industrial NAND types.
• Optional eMMC or on-board flash for low-maintenance systems.
Lifecycle, Maintenance
• Long product lifecycle (typically 5–10+ years availability of the same board revision).
• Long-term availability of the CPU platform (CPU manufacturers' embedded roadmaps).
• Consistent BOM management: controlled component changes, important for regulatory approvals.
• Remote management capabilities (e.g., AMT, IPMI-like functions, out-of-band management on some industrial Mini-ITX boards).
• Easy on-site maintenance: easily accessible connectors, clearly documented pinout.
Security, Software, Certification
• Support for Secure Boot, TPM, and encryption to prevent tampering.
• Compatibility with real-time operating systems, industrial Linux distributions, and Windows IoT.
• Certifications depending on the industry (EMC standards for industrial applications, medical standards, and, where applicable, automotive standards such as E-Mark).
Form Factor
• Standardized dimensions of 170 x 170 mm, enabling easy integration into compact Box PCs, kiosks, panels, vehicles, and machines.
• Low profile, e.g., flat heat sinks, horizontal RAM modules, and low-profile connectors (important for 1U enclosures or very slim boxes).
• Mounting points: robust mounting holes, some with additional mounting points for vibration resistance.
• Front/backplane orientation of the connectors ensures optimal access to all I/Os.
Advantages of the Mini-ITX Form Factor, especially in Industrial Applications
• Very compact yet offering full x86 performance, making it ideal for edge computing, HMI panels, and compact controllers.
• Good balance between expandability (PCIe slot, M.2, miniPCIe) and footprint.
• High energy efficiency and therefore reduced cooling requirements, important in enclosed boxes or control cabinets.
• Wide range of applications: from simple IoT devices to high-performance vision systems, depending on the CPU class and expansion cards selected.
Disadvantages of the Mini-ITX Form Factor
• Due to their dimensions, Mini-ITX boards are not suitable for very small devices. Depending on the required functionality, 3.5" or 2.5" boards may be more appropriate.
• Many Mini-ITX boards available on the market only partially meet the requirements for industrial boards and are more accurately classified as "light industrial boards."
• Most manufacturers of Mini-ITX boards require minimum order quantities for economical production, which often far exceed the project volumes of their customers.
Mini ITX Boards at 1ST-embedded
Now it's your turn: get informed and use the Mini ITX Boards successful in your industrial applications!
Consult your expert: Sven Trommer
, Tel. +4940-7003550
We look forward to hearing from you!
Jelena Dronowa, Head of Digital Media, Dipl.-Ing for Systems Engineering
